Difference between revisions of "WEP Cracking"
From ivc wiki
Jump to navigationJump to search
| Line 9: | Line 9: | ||
Parts: | Parts: | ||
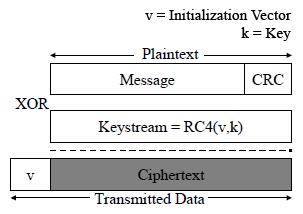
* '''WEP encryption''': 24-bit unencrypted initialization vector + 104-bit key (13 characters/bytes), 128-bit key | * '''WEP encryption''': | ||
* '''ARP replay''': On the basis that the first 12-bytes of ARP packets always stays the same | # 24-bit unencrypted initialization vector + 104-bit key (13 characters/bytes), 128-bit key | ||
* '''Key attack''': Find initialization vector collisions where two ARP ciphertexts are the same (2^24 possibilities) | # Used to generate RC4 cipher stream -> XOR the message -> Encrypted packets | ||
* '''ARP replay''': | |||
# On the basis that the first 12-bytes of ARP packets always stays the same | |||
# Capture one ARP packet | |||
# Inject back to into the network to stimulate traffic | |||
# 10-20000 packets enough ARP packets and initialization vector | |||
* '''Key attack''': | |||
# Find initialization vector collisions where two ARP ciphertexts are the same (2^24 possibilities) | |||
# XOR back first 12-bytes using the known plain-text ARP data | |||
# RC4 stream cipher is revealed for that specific IV | |||
# Gather enough collisions -> Use the collected data to build a database of IVs and RC4 stream ciphers to gain a factor by statistical analysis and guess each byte in the final 104-bit (13 character) key | |||
# Try key to verify decryption of captured encrypted packets | |||
== References == | == References == | ||
Revision as of 23:46, 26 August 2009
WEP is infamously known as the broken wireless security protocol. A design flaw was discovered in 2001 and after several cascading discoveries it's now possible to crack a WEP protected network within minutes. WPA is the successor to WEP and features a better but not perfect security protocol.
Background
There are now many sources that describe the vulnerability in detail and APR replay to generate traffic, but this is a short summary. For an throughout explaination on how WEP is implemented and the vulnerabilities, see the link below.
Parts:
- WEP encryption:
- 24-bit unencrypted initialization vector + 104-bit key (13 characters/bytes), 128-bit key
- Used to generate RC4 cipher stream -> XOR the message -> Encrypted packets
- ARP replay:
- On the basis that the first 12-bytes of ARP packets always stays the same
- Capture one ARP packet
- Inject back to into the network to stimulate traffic
- 10-20000 packets enough ARP packets and initialization vector
- Key attack:
- Find initialization vector collisions where two ARP ciphertexts are the same (2^24 possibilities)
- XOR back first 12-bytes using the known plain-text ARP data
- RC4 stream cipher is revealed for that specific IV
- Gather enough collisions -> Use the collected data to build a database of IVs and RC4 stream ciphers to gain a factor by statistical analysis and guess each byte in the final 104-bit (13 character) key
- Try key to verify decryption of captured encrypted packets