MakerBot
The MakerBot is an open source 3D-printer. Great for experimenting with designs and small manufacturing. The latest model, Thing-O-Matic, has improved accuracy and expanded electronics.
Schematics
Electronics
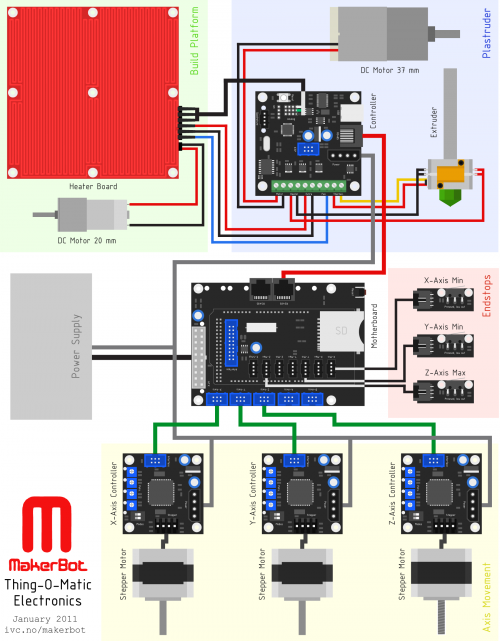
All the electronics is neatly hid away under the build platform, including the power-supply. The overview below shows all the components and how they are all connected.
- Download Thing-O-Matic Electronics - PDF vector version
Symbols
All the components below has been compiled into a Frizing library to be used for prototyping. The original illustrator files is in the second link.
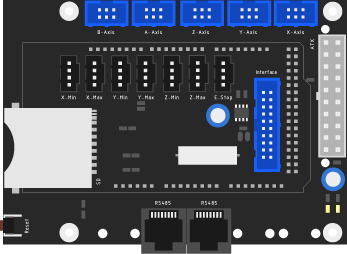
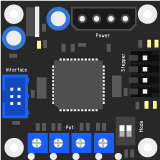
Motherboard
The main board connects the Arduino controller with an external USB-interface, a SD-card slot, drives the stepper-controllers and extruder controller.
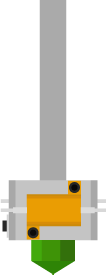
Extruder
Has inputs from the thermalcouple temperature measuring probe, power MOSFETs to drive the main heater to melt plastic and heat the assembly board. Auxiliary connections for controlling the automated assembly plate and heat sensor for the board temperature.
On top of the extruder is the feed for the plastic, driven by a DC-motor from the extruder controller. The heat element is a long piece of metal tube to keep the heat and melting process even. Two heat resistors exerts heat onto the main metal block before the plastic is extruded through a narrow nozzle. The thermocouple is mounted on the main block.
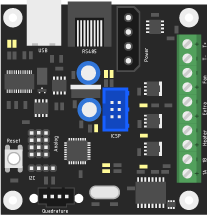
Stepper Controller
To drive the stepper motors, a controller can control the motion of the axis down to an accuracy of 1.8 degrees per step. The operation can be fine tuned using 4 potentiometers on the controller. Two dip-switches determine the type of stepper-motor that will be attached.
End stops
Each axis has an end-stop to signal when its at the farthest/closes range.
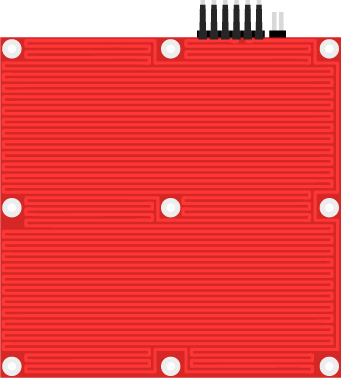
Heaterboard
To keep the plastic from shrinking during the printing process, the base where the object sits is heated by a copper maze on the board. A thermistor underneath is monitoring the temperature. On the automated model the base can roll out when the object is finished.